Introduction
In this blog post, we will explore 40 essential laboratory instruments or apparatus used in diverse applications across various fields like biology, chemistry, testing firms, and environmental monitoring stations. These tools, employed in laboratory settings, play a vital role in conducting experiments, analyzing samples, and ensuring accurate results.

1. Electronic Precision Balance
The electronic precision balance is a crucial instrument for weighing samples accurately. It offers different levels of accuracy, allowing measurements at one percent, one thousandth, one ten thousandth, and even one hundred thousandth increments. This precision makes it suitable for a variety of scientific applications.

2. Sterilization Chamber
Before and after laboratory procedures, it is essential to ensure the sterilization and disinfection of instruments. The sterilization chamber serves this purpose effectively, maintaining a controlled environment that eliminates any potential contaminants.

3. Centrifugal Device
For separating mixtures containing liquid and solid particles or separating various liquid components, a centrifugal device is employed. It utilizes centrifugal force to achieve efficient separation, enabling researchers to isolate specific substances for further analysis.
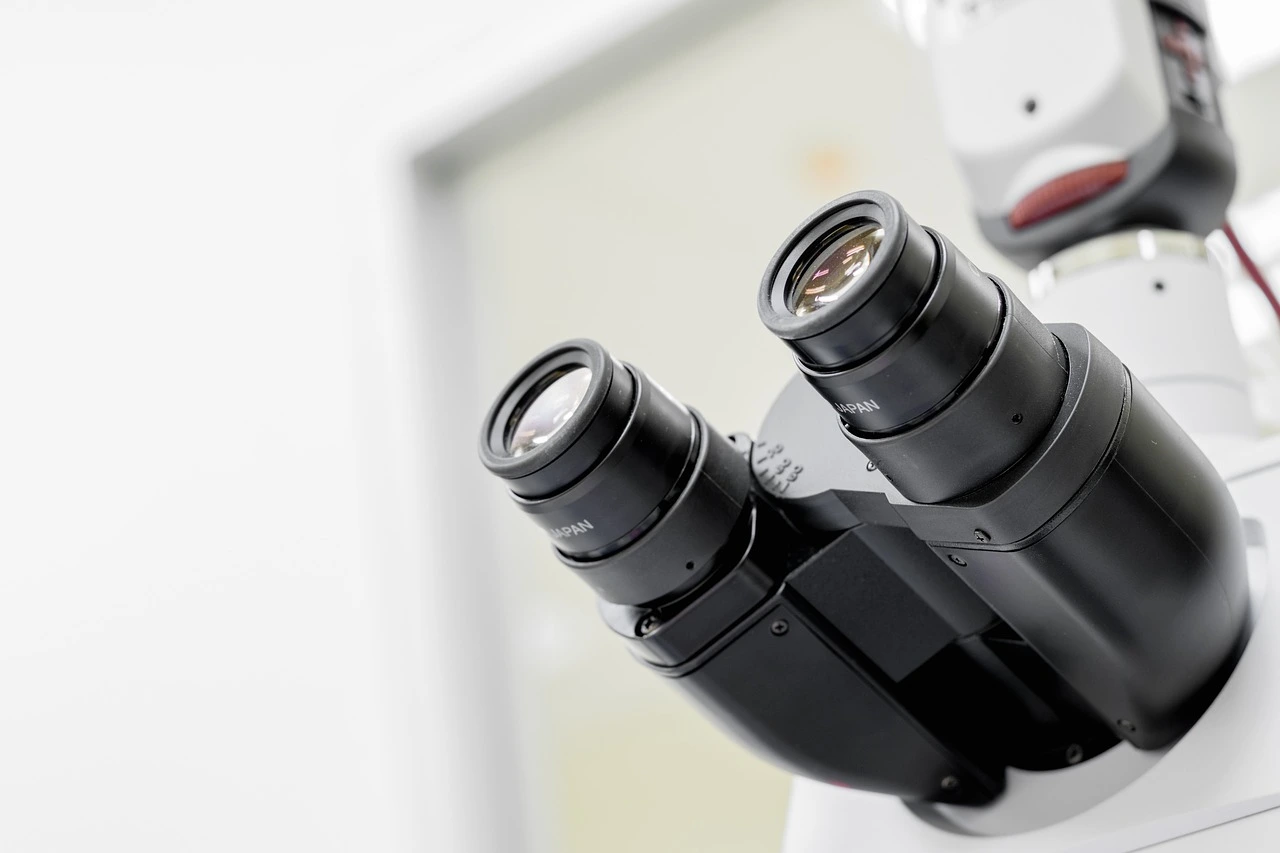

4. Optical Magnifier
An optical magnifier is a valuable tool used to enlarge and observe samples under microscopic examination. It assists researchers in studying intricate details and structures, aiding in the identification and analysis of various specimens.
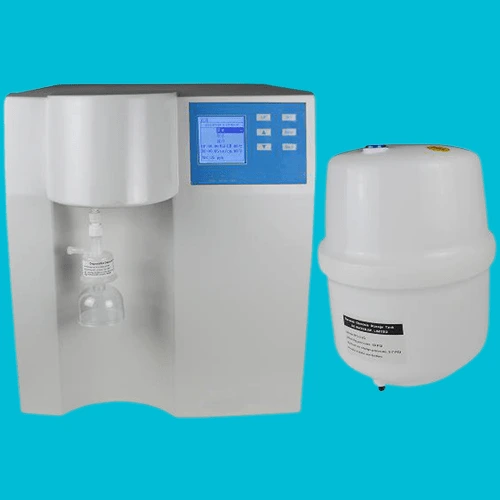

5. Ultra-Purification Water System
In laboratory settings, the need for pure or ultra-pure water is paramount. The ultra-purification water system ensures the production of water with exceptional quality, meeting the stringent requirements of scientific experiments and analyses.
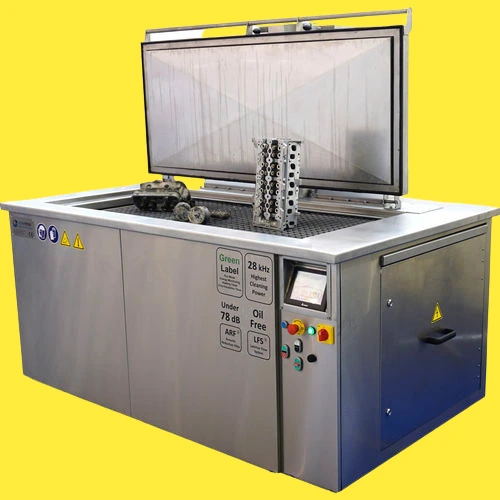

6. Ultrasonic Cleansing Device
Laboratory glassware and equipment often require thorough cleaning to remove contaminants and residue. The ultrasonic cleansing device employs ultrasonic waves to achieve deep cleaning, ensuring the instruments are ready for subsequent use.

7. Visible Light Spectrophotometer
For both quantitative and qualitative analyses of substances, the visible light spectrophotometer is an indispensable instrument. It measures the interaction of substances with visible light, providing valuable insights into their properties and composition.

8. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
The UV-Vis spectrophotometer is designed to measure the absorption exhibited by substances in response to monochromatic radiation of varying wavelengths. This instrument enables precise quantitative analysis, aiding researchers in understanding the characteristics of various compounds.

9. Atomic Absorption Spectrometer
Quantitative analysis of the absorption levels of characteristic radiation emitted by ground state atoms of measured elements is made possible with the atomic absorption spectrometer. It provides valuable data on element concentrations, facilitating research in fields like environmental monitoring and material analysis.

10. Atomic Fluorescence Photometer
For the trace analysis of specific elements within samples, the atomic fluorescence photometer is employed. It enables the detection and measurement of elements such as arsenic, mercury, selenium, and more, offering insights into their presence and concentrations.

11. Gas Chromatography System
The gas chromatography system is a versatile instrument that allows the separation and analysis of complex mixtures. It features customizable configurations tailored to specific measurement requirements, making it an essential tool for various scientific disciplines.
12. Ion Chromatography Device
The measurement of both anions and cations is made possible by the ion chromatography device. It enables the analysis of ions present in a sample, providing valuable information about the composition and concentration of various substances.

13. Magnetic Stirring Apparatus
Achieving stable and consistent stirring of liquid solutions is crucial in many laboratory processes. The magnetic stirring apparatus utilizes a rotating magnetic field to create agitation, ensuring thorough mixing of reagents and substances.
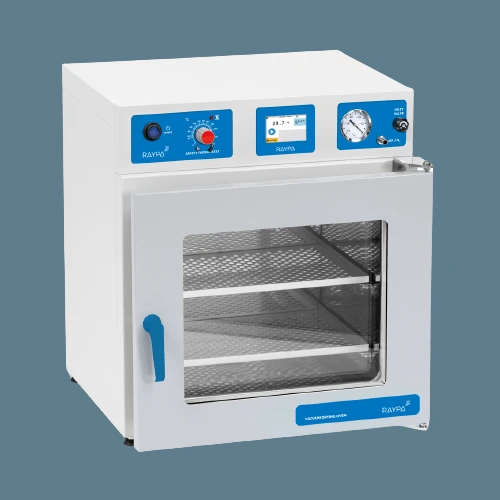

14. Vacuum Drying Oven
In laboratory settings, diverse glass containers often require drying, baking, disinfection, and sterilization. The vacuum drying oven provides a controlled environment for these processes, ensuring efficient and reliable results.
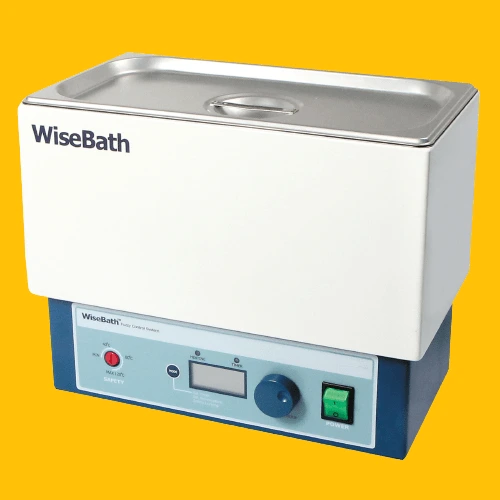

15. Water Bath
The water bath is a versatile instrument employed for various applications, including drying, concentrating, distilling, and facilitating constant temperature heating and temperature tests. It offers researchers a controlled environment for specific procedures.

16. Nitrogen Concentrator
Concentrating samples is often necessary for laboratory analyses, and the nitrogen concentrator serves this purpose. By utilizing nitrogen gas, it facilitates the concentration of samples, improving the efficiency and accuracy of subsequent analyses.
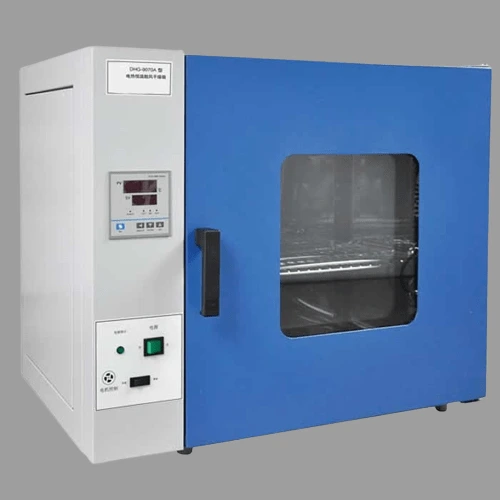

17. Electric Forced-Air Drying Oven
For baking, drying, heat treatment, and thermal processing of various objects, the electric forced-air drying oven is a reliable choice. It provides researchers with precise control over temperature, ensuring optimal conditions for specific procedures.
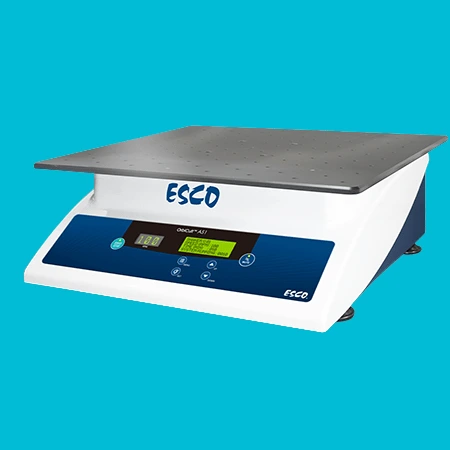

18. Oscillation Platform
The oscillation platform is used for the vibrational cultivation of diverse liquid and solid compounds. It finds applications in biology, biochemistry, and other fields where controlled oscillation is necessary for cultivating cells and strains.
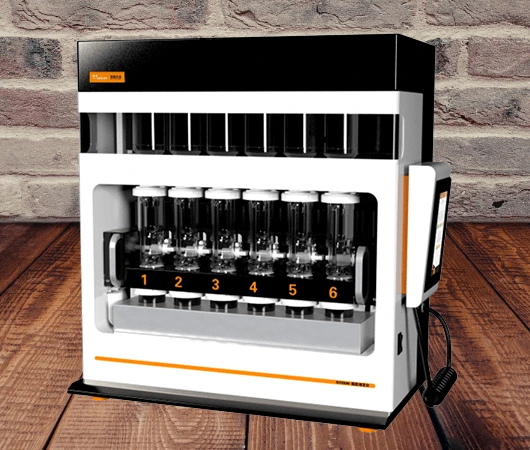

19. Lipid Analyzer
Accurately measuring lipid content is essential in many research areas, including nutrition and biochemistry. The lipid analyzer is a specialized instrument designed precisely for this purpose, providing researchers with precise and reliable data.
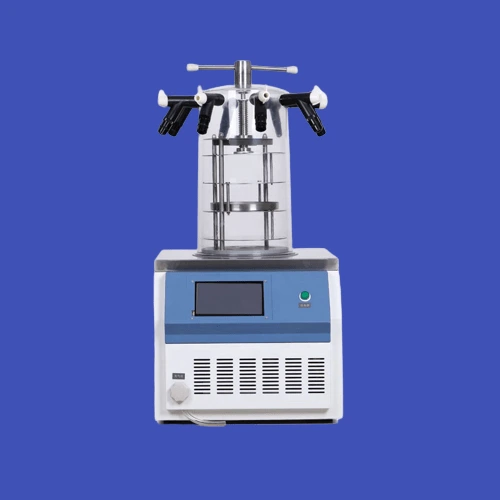

20. Cryogenic Freeze Dryer
Preserving biological samples, tissues, and various specimens often requires the use of a cryogenic freeze dryer. It utilizes low temperatures to freeze samples and subsequently removes moisture through sublimation, ensuring the long-term storage of valuable materials.
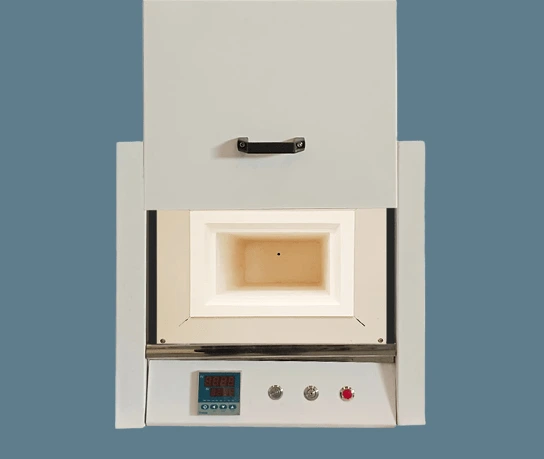

21. Refractory Furnace/Box-Type Resistance Furnace
The refractory furnace or box-type resistance furnace is employed as a heating and drying apparatus in laboratory settings. It provides controlled heating conditions, enabling researchers to execute specific processes accurately.
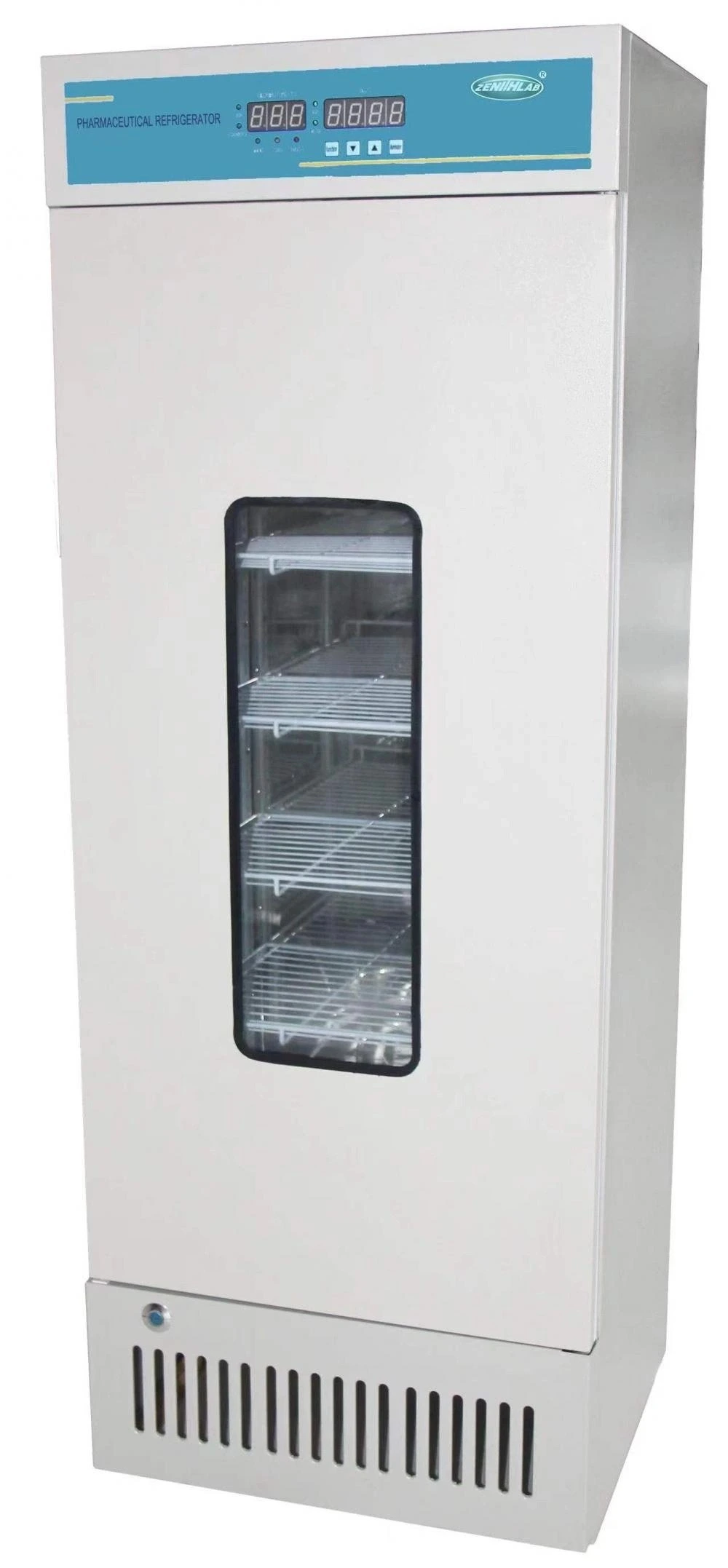

22. Biochemical Incubator
Maintaining the ideal conditions for the storage of culture media, microbial cultures, and environmental tests is crucial in laboratory work. The biochemical incubator offers a controlled environment with regulated temperature and humidity, promoting optimal growth and development.

23. Electric Heating Plate
For the simultaneous processing of multiple samples, the electric heating plate is a valuable instrument. It ensures uniform heating across each heating point, allowing researchers to conduct experiments efficiently.

24. Distillation Apparatus
The distillation apparatus is employed for the treatment of samples before determining specific substances. It enables researchers to separate and purify compounds such as ammonia nitrogen, volatile phenol, and cyanide, among others.
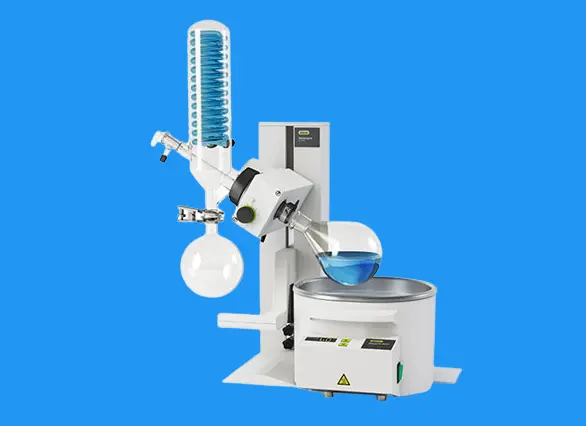

25. Rotary Evaporator
The rotary evaporator utilizes vacuum distillation techniques to heat, diffuse, and evaporate solvents within a rotary flask under negative pressure. It facilitates the separation of solutions and solvents, making it a vital tool in laboratory research.

26. Ultra-Low Temperature Freezer
When samples require storage at extremely low temperatures, the ultra-low temperature freezer is the instrument of choice. It is suitable for preserving biological materials, vaccines, reagents, bacteria, and other samples, ensuring their integrity and longevity.
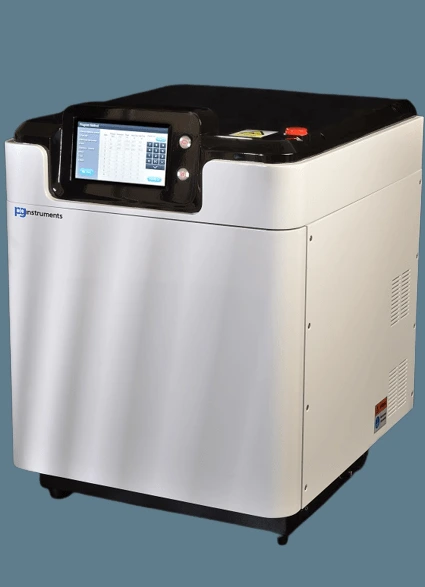

27. Microwave Digestion System
Reducing the preparation time for samples is crucial in many laboratory processes. The microwave digestion system employs microwave heating to accelerate the reaction time of reagents and samples, facilitating efficient sample preparation.

28. Solid-Phase Extraction System
The solid-phase extraction system is used for the extraction of samples, enabling researchers to isolate specific compounds of interest. It plays a crucial role in sample preparation for subsequent analyses and purification processes.

29. Grinding Apparatus
For the extraction and purification of original DNA, RNA, and protein from various sources, the grinding apparatus is employed. It assists researchers in breaking down samples, enabling the extraction of essential genetic and biochemical materials.

30. Ball Mill
The ball mill is a versatile instrument used for mixing, finely grinding, and preparing samples. It finds applications in various fields, including material science and pharmaceutical research, allowing researchers to achieve desired particle sizes and homogeneity.
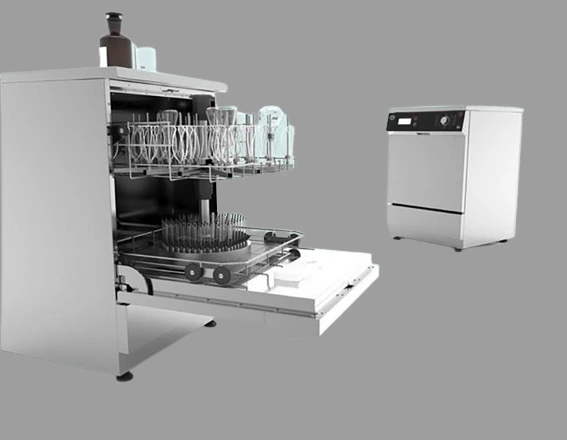

31. Bottle Washer
Proper cleaning of glass and plastic containers is essential in laboratory settings. The bottle washer is specialized equipment designed for cleaning bottles using brush cleaning and water flushing techniques, ensuring optimal hygiene and reusability.

32. pH Meter
Measuring the pH levels in aqueous solutions is crucial in many laboratory analyses. The pH meter provides researchers with accurate and reliable data, allowing them to monitor and adjust the acidity or alkalinity of samples.
33. Conductivity Meter
The conductivity meter is employed for measuring the electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions. It assists researchers in assessing the ionic strength and the presence of dissolved substances, providing valuable insights into the properties of the solution.

34. Bacterial Colony Counter
Accurate counting of bacteria in samples is essential in microbiology and related fields. The bacterial colony counter is a digital display instrument specifically designed for this purpose, ensuring precise and efficient counting of bacterial colonies.

35. Ultra-Clean Laminar Flow Cabinet
In specific work areas requiring stringent cleanliness standards, the ultra-clean laminar flow cabinet is employed. It provides a controlled environment with HEPA-filtered air, preventing contamination and ensuring the safety of sensitive experiments.

36. Water-Resistant Incubator
Detecting heat-resistant coliform bacteria is crucial in water quality testing. The water-resistant incubator provides a controlled environment for the detection and cultivation of bacteria, promoting accurate analysis and assessment.
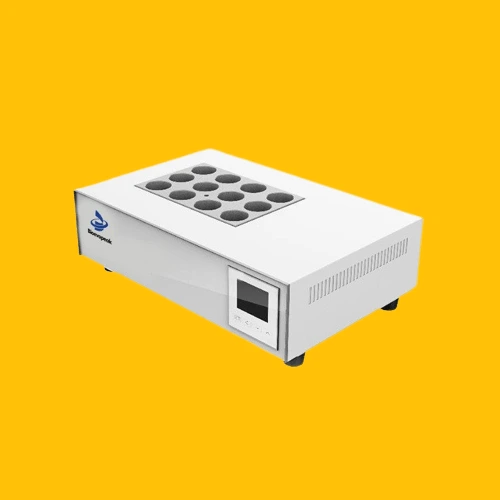

37. Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Constant Temperature Heating Apparatus
The chemical oxygen demand constant temperature heating apparatus is designed for precise and consistent heating of samples during COD measurements. It ensures stable and accurate results in environmental analysis and water quality monitoring.
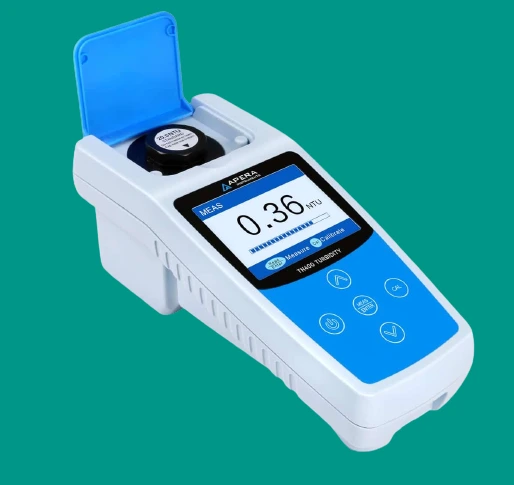

38. Turbidity Meter
The turbidity meter is used to measure the clarity of liquids by determining the amount of light scattered by suspended particles. It is widely employed in water quality testing and environmental monitoring, providing insights into the presence and concentration of particulate matter.
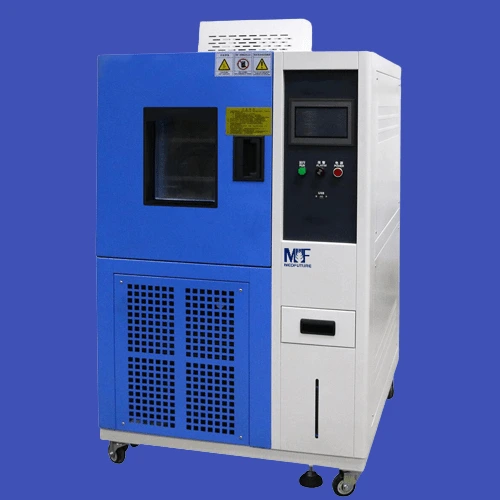

39. High and Low-Temperature Testing Chamber
For evaluating the performance and stability of materials under extreme temperature conditions, high and low-temperature testing chamber is employed. It allows researchers to simulate and analyze the effects of temperature on various substances.
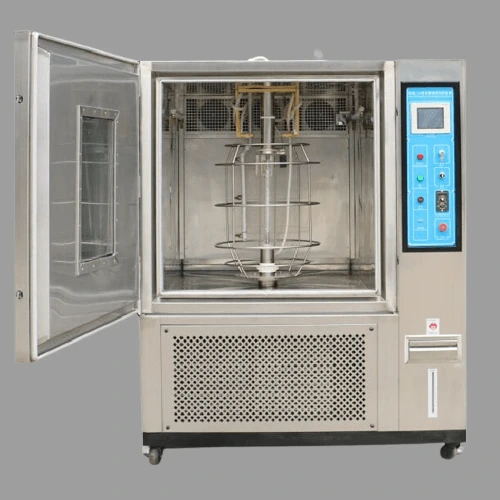

40. Aging Testing Chamber
The aging testing chamber is utilized to assess the long-term durability and performance of materials and products. It creates controlled environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure, enabling researchers to evaluate aging effects over time.

Conclusion
Laboratory instruments are essential tools that enable scientists and researchers to carry out precise experiments, analyses, and investigations. The instruments shortly discussed in this post cover a wide range of applications, including weighing, separation, analysis, purification, heating, storage, and more. By utilizing these instruments, researchers can ensure accurate results and make significant advancements in their respective fields of study.

FAQs
Q1. What is the purpose of an electronic precision balance in a laboratory?
A: An electronic precision balance is used in a laboratory to weigh samples accurately. It provides different levels of precision, allowing measurements at various increments. This instrument is crucial for ensuring accurate measurements in scientific experiments and analyses.
Q2. What is the function of a sterilization chamber in a laboratory?
A: A sterilization chamber is used to sterilize and disinfect instruments before and after laboratory procedures. It creates a controlled environment that eliminates potential contaminants, ensuring the safety and integrity of experimental setups and samples.
Q3. How does a centrifugal device work in a laboratory?
A: A centrifugal device utilizes centrifugal force to separate mixtures containing liquid and solid particles or separate different liquid components. It spins samples at high speeds, causing the denser particles or components to move outward, facilitating efficient separation.
Q4. What is the purpose of an optical magnifier in a laboratory?
A: An optical magnifier is used in a laboratory to enlarge and observe samples under microscopic examination. It aids researchers in studying intricate details and structures, allowing for the identification and analysis of various specimens.
Q5. Why is an ultra-purification water system important in a laboratory?
A: An ultra-purification water system is essential in a laboratory to produce water with exceptional quality. It removes impurities and contaminants, meeting the stringent requirements of scientific experiments and analyses that demand pure or ultra-pure water.

